Here’s an intelligence report on some of the most persistent and sneakiest garden weeds of Michigan gardens. To pack the most information into available space, we’ll let pictures and vital statistics do the talking.
Most Persistent
Bindweed, Canada thistle, Ground ivy, Mexican bamboo,
Nut sedge, Scouring rush, Violets, and Wild garlic
These are some of the warriors you’ll have to kill and kill again. They are weeds that cause people to shake their heads even as I answer their question, “How do I get rid of…” The gardener may even smile ruefully while saying over and over, “No, I’ve tried that.”
If you’ve battled these and been beaten, I don’t doubt you’ve tried, but I do doubt that you understood and matched the persistence of your foe. Cut off their heads—their green, leafy source of energy—and they sprout anew from deep, extensive root systems like the mythical beast which sprouted two heads each time one was cut. Each cutting, digging or herbicide application by the gardener puts a drain on the roots’ starch reserves, but each day a new shoot gathers sun, it replenishes those roots. If you attack just once, twice or three times a year and let the survivors surface and gather sun for weeks or months during the cease-fires, you insure a perpetual war.
To best the beasts on this list, beat them at their own game. After you roust out every bit of green and as much root as you can reach, post a guard. Expect new shoots within a week. Find them and cut them before they can return to the root the starch they used in reaching the sun. Be vigilant in this follow up and you will gradually exhaust the weed’s reserves.
Wild Garlic
Wild garlic (Allium vineale), which hides its narrow foliage among grass blades, can always be identified by its smell. Survives mowing as well as grass, escapes broadleaf weed killers, and stores enough energy in the bulb to return repeatedly if weeders leave the bulb behind. Infestations are usually best handled by killing or digging out all vegetation in the area and then maintaining a thick mulch and a weeding vigil for 18 months.
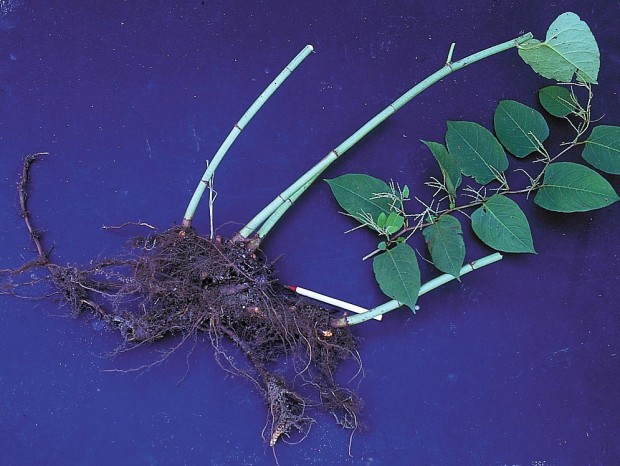
Mexican bamboo
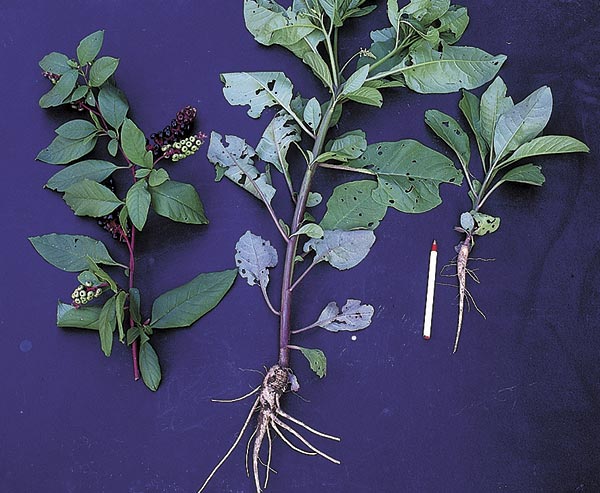
Mexican bamboo, Japanese knotweed (Polygonum cuspidatum). Perennial, up to 9 feet tall, spreading far and wide from established clumps by stout underground runners (left). Jointed, hollow stems explain the common name “bamboo.” The center section of stem has been eliminated in this photo for clarity’s sake. Grub out the roots or apply Roundup and be prepared to kill remnant sprouts for a season or two.
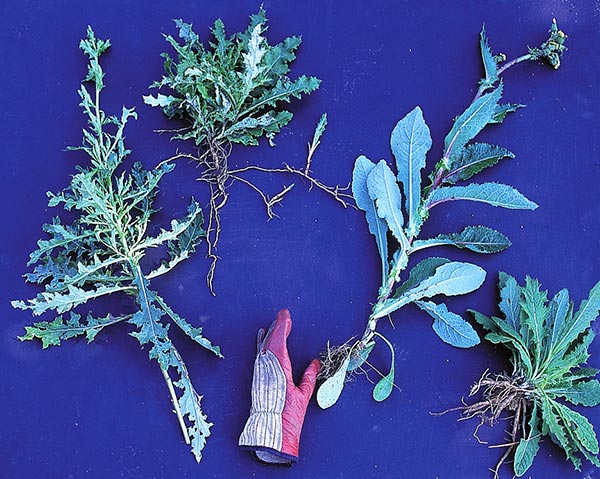
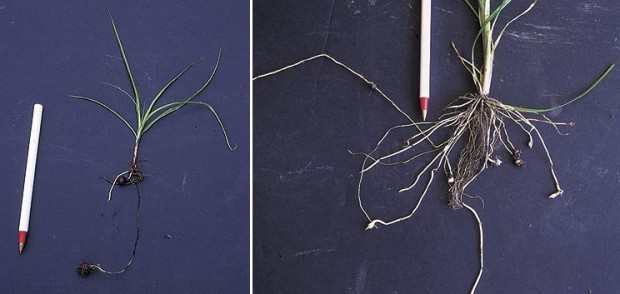
Canada thistle
Perennial, wickedly persistent Canada thistle—Cirsium arvense, which is not native, despite its common name. A stem and a basal clump are shown here, left of the glove. Note the running roots, which can persist and keep sprouting even through a year or two of frequent pulling or spraying with herbicide. The key to control is to be even more persistent than the plant and to adopt as a mantra what Edwin Spencer writes in All About Weeds, “…any plant can be killed—starved to death—if it is not permitted to spread its leaves for more than a few days at a time.” The annual prickly sow thistle (Sonchus aspera), immediately right of the glove, and biennial bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare), far right, are weedy but not nearly so much trouble to eliminate. Just keep pulling or cutting the annual and biennial thistles before they set seed, and keep the area well mulched to prevent existing seed in the soil from sprouting.
Violet
Violet, common blue violet (Viola sororia). Perennial, often tolerated in gardens for its blue-violet flowers in spring, yet hated for colonizing nearby lawn. A typically schizophrenic approach by gardeners! Either accept it in both places or eliminate it from both. Like ground ivy, it can be killed in lawns with broadleaf weed killer—may take repeated applications—but will then return from seed if the grass is not pampered until thick enough to shade out the seedlings.
Nut Sedge
Perennial nut sedge or yellow nutgrass (Cyperus esculentus) infuriates gardeners by returning even if pulled and pulled again. But of course it returns if the soil is not loosened deep and well so that the brown nut-like tubers come out, too. In the inset photo, note the horizontally-running root, which turns up to produce a second clump of “grass” and the new crop of nuts developing as white bulbs at root tips. Nuts can rest dormant for many years in the soil and be revived by deep excavations. Frightening to think nut sedge tubers are edible and somewhere a large-tuber form may be in development as a food crop!
 Ground ivy
Ground ivy
Ground ivy, also called gill-over-the-ground, is Glechoma hederacea, a perennial. It snakes through lawn, rooting where its stems make contact with bare soil. In gardens, freed from a mower’s restraint, it explodes to become a dense mat and can weave its way 18 inches up into stems of other plants. Shallow-rooted, it’s easily pried loose from beds and mulch will prevent it from reestablishing by seed. However, it must also be banned from adjacent lawns. The broadleaf weed killer Trimec will kill it, but the lawn must then be overseeded and thickened by better care lest ground ivy seed simply sprout and re-take the bare soil between grass plants. Sometimes confused with henbit, an annual.
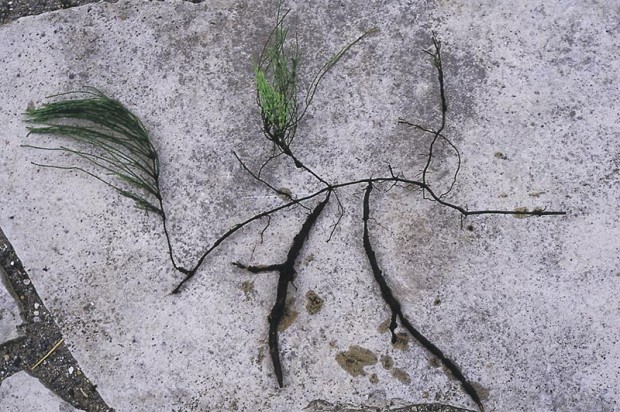
Scouring rush
Field horsetail, or scouring rush (Equisetum arvense), is a native perennial often brought into gardens in tree and shrub root balls. Easiest to eradicate if caught early in its tenure on a property, otherwise it must be dug and surviving pieces starved by repeated pulling.
Bindweed flower
The trouble with focusing on flowers for identification is that the worst weeds—long-lived perennials that are slow to begin blooming—can become entrenched before we know what we’re facing. Once great bindweed (Convolvulus sepium) is large enough to show its two-inch white or pinkish flowers, it’s so well-grounded that its removal will require a two- to
three-year pitched battle.
Bindweed
Convolvulus sepium, the great bindweed (pictured) and its smaller-flowered, smaller-leaved, lower reaching cousin C. arvensis, small-flowered bindweed. Perennial. Extensive, deep, easily broken root systems. My own experience mirrors that of W. C. Muenscher who writes in the textbook Weeds, “Clean cultivation…if performed thoroughly, will control bindweed in two years. The land must be kept black, that is no green shoots should be allowed to appear above ground. Cultivation should be at frequent intervals of about six days. Under certain conditions this time may be extended a few days and under other conditions it may have to be shortened to three- or four-day intervals.
Sneakiest
Enchanter’s nightshade, Glossy buckthorn,
Pokeweed, and Yellow wood sorrel
These weeds earned places on this list by their tendency to present a false face or ride in on invited guests. Once their true natures and their avenues of entry into a garden are known, they are relatively easy to eradicate with informed pulling and thorough mulching.
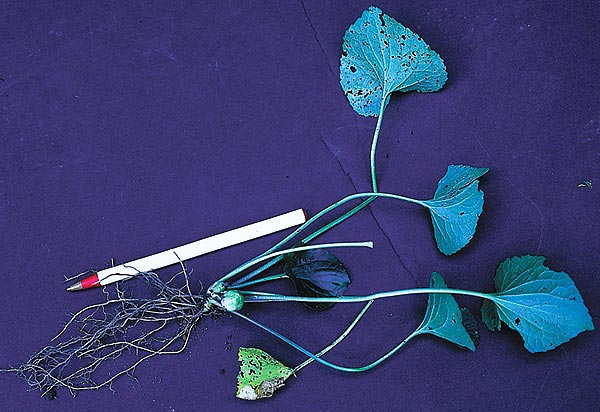
Pokeweed
Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana) is an impressive, statuesque plant draped in purple-black berries in fall. Birds love this native fruit – although it is quite toxic to humans – but gardeners wish their feathered friends would eat all of the berries before they fall and then not excrete any! This photo shows the berries of an established plant – up to 9 feet tall and wide – and the roots of seedlings just 4 months old (center) and one month old (right). The roots don’t run but they do delve deep, so pull them early or be prepared to dig deep.
Enchanter’s nightshade
The native perennial, enchanter’s nightshade (Circaea canadensis) is rarely seen in sunny gardens but can drive a shady gardener wild, especially when the buried seeds ripen (right photo). In seed, it seems to pull out easily and completely, but careful loosening of the soil before pulling will reveal the new, white, nearly-detached perennial roots (left photo) which can lie quietly until the next spring.
Glossy buckthorn
Glossy buckthorn (Rhamnus cathartica) is a small tree with very bad habits. It leafs out early in spring and keeps its leaves far into fall, effectively shading out native plants wherever it sprouts. Since it can thrive in woods, sun, wet areas and dry, it’s a serious threat to native ecosystems of all kinds, as well as gardens. The seeds don’t travel far on their own. Birds eat and then drop them where they roost so the trees are common along fence lines. Fast growing, the gardener must patrol for and pull them at least once a year, and try to locate and remove the mature plants which are providing the shiny black berries. One thing gardeners can be thankful for is the plant’s shallow, fibrous root system – far easier to pull than other woody weeds such as mulberry and tree of heaven.
 Yellow wood sorrel & Common wood sorrel
Yellow wood sorrel & Common wood sorrel
Yellow wood sorrel, right, (Oxalis europaea) seems frail and easy to pull, compared to its ground-hugging cousin, common wood sorrel, below, (Oxalis stricta). But like enchanter’s nightshade, the yellow wood sorrel has a deceptive root system. Pull it and it seems to come up easily, roots and all. Yet if one loosens the soil well before pulling and uses a light touch, it becomes clear how many fragile, white, running perennial roots can be left behind by the uninformed gardener. Far easier to deal with is the common wood sorrel, which does not spread below ground but only above where stems sit on moist soil and root (the pen points to such a stem).